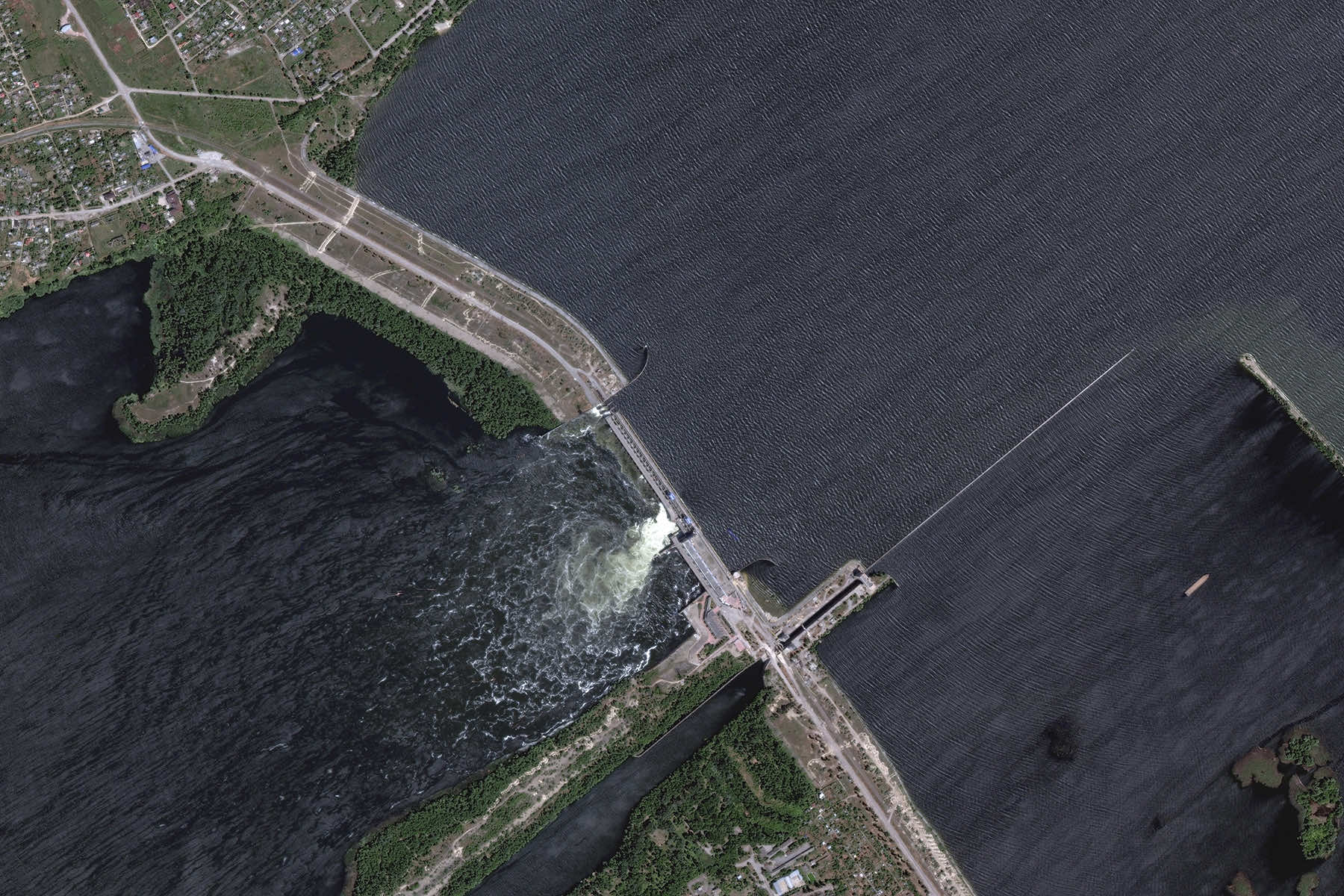
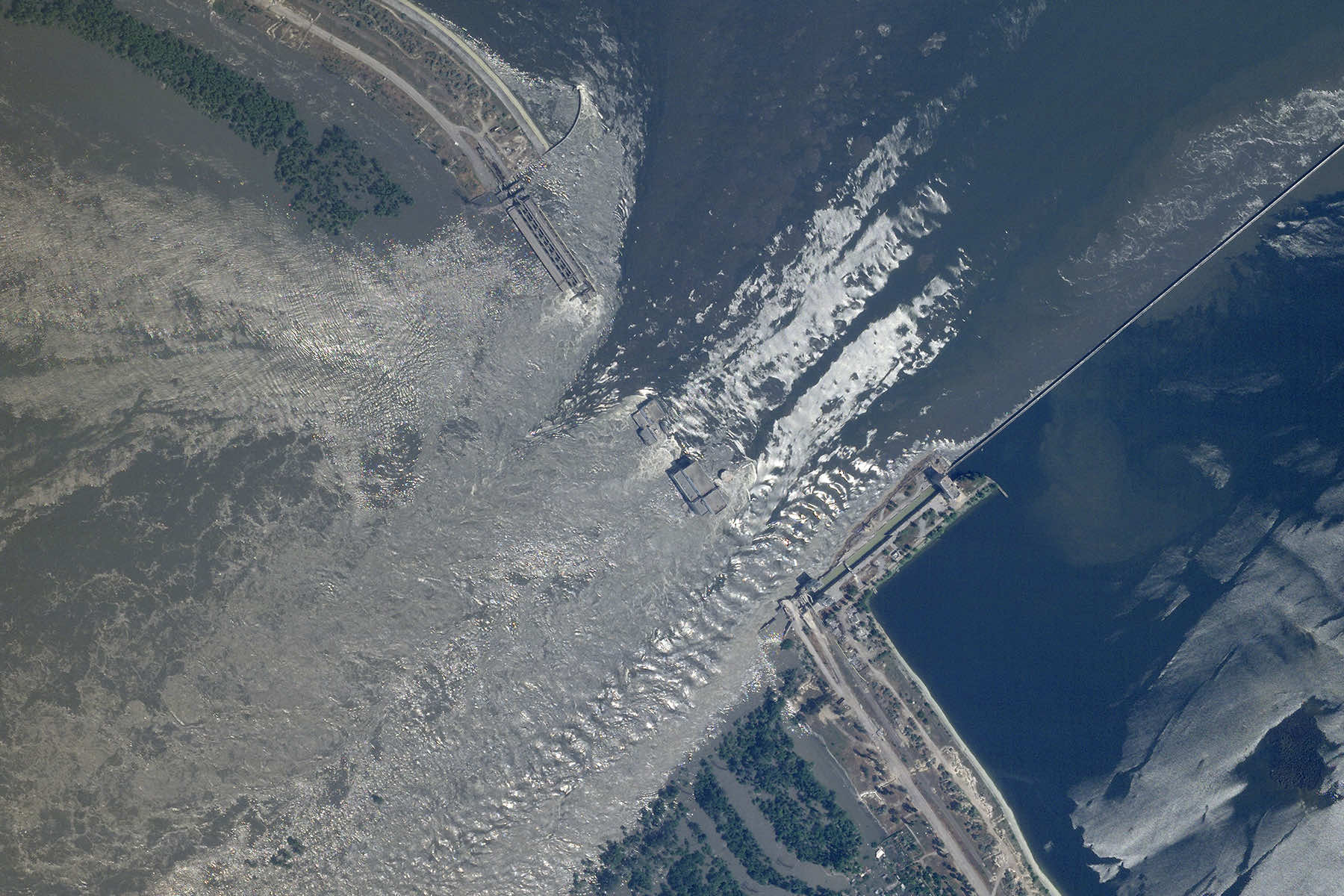
Global prices for wheat and corn soared on June 6 after a major dam in Ukraine collapsed, renewing market fears about the fragility of the country’s ability to ship food to Africa, the Middle East and parts of Asia as it fights a war with Russia.
Wheat prices gained 2.4% in early trading on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, to $6.39 a bushel. The cost of corn rose more than 1%, to $6.04 a bushel, and oats gained 0.73%, to $3.46 per unit. Prices were higher earlier in the day but faded.
The destruction of the Kakhovka dam and hydroelectric power station, which sits in a Russian-controlled area on the Dnieper River, raised concerns about disruption to Ukraine’s affordable supplies of wheat, barley, corn and sunflower oil getting to developing nations where people are struggling with hunger and high food prices.
“Anytime this war shows signs of getting further escalated, there’s a lot of concern,” said Joseph Glauber, senior research fellow at the International Food Policy Research Institute. “Markets react to that.”
Ukraine and Russia are both major agricultural suppliers and the war’s disruption to their exports worsened a global food crisis tied to droughts and other factors. Breakthrough agreements brokered by the U.N. and Turkey last year got food moving again through the Black Sea, but it’s faced setbacks.
Russia briefly pulled out of the deal last year, has threatened to leave again, is accused of slowing shipments from Ukraine and has only agreed to renew the deal for two months at a time.
“People are going to be watching to see what happens with the agreement,” said Glauber, former chief economist at the U.S. Department of Agriculture. “This reminds everyone that it’s not just pro forma, that this could be a very serious development if indeed the agreement is broken.”
There are massive agricultural fields in southern Ukraine where the dam burst, and while the collapse has endangered crops in the path of the floodwaters, Glauber says less wheat has been planted in that area because it’s near the fighting and a lot is growing elsewhere.
The collapse has threatened drinking water supplies, with officials also warning of a looming environmental disaster — pointing to oil escaping from the dam machinery and significant flooding.
Andrey Sizov, managing director of Black Sea agricultural markets research firm SovEcon, said the dam collapse looked “like a big escalation with dire consequences and huge headline risk.”
Wheat, vegetable oil, and other food commodity prices have fallen from record highs last year after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine — thanks in part to the Black Sea grain deal — but the relief in prices has not made it to markets, grocery stores and kitchen tables.
Citi commodities analysts called the dam breach a “reminder of lingering inflationary risk in the goods market.”
It’s possible temporary jumps in prices follow significant news events, like the dam collapse, analysts say.
But circumstances are key — and expectations for food exports from Ukraine will likely “continue to diminish as we recognize that Ukrainian production will continue to be severely impaired because of the war,” said Joe Janzen, assistant professor at University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign’s College of Agricultural, Consumer and Environmental Sciences.
The supply of grain Ukraine is able to export is 40% lower than it was two years ago, Glauber said.