“The Supreme Court ruling was an unprecedented assault on a woman’s constitutional rights. Complete strangers will now be empowered to inject themselves in the most private and personal health decisions faced by women.” – President Joe Biden
In May, Governor Abbott signed the strongest anti-abortion law in the country, Senate Bill 8, which went into effect on September 1. It bans abortion after 6 weeks — when many women do not even know they are pregnant — thus automatically stopping about 85% of abortions in Texas. There are no exceptions for rape or incest. Opponents of the bill had asked the Supreme Court to stop the law from taking effect. It declined to do so.
The law avoided the 1973 Supreme Court Roe v. Wade decision protecting the right to abortion before fetal viability at about 22 to 24 weeks by leaving the enforcement of the law not up to the state, but rather up to private citizens. This was deliberate. As Dahlia Lithwick and Mark Joseph Stern explained in an article in Slate: “Typically, when a state restricts abortion, providers file a lawsuit in federal court against the state officials responsible for enforcing the new law. Here, however, there are no such officials: The law is enforced by individual anti-abortion activists.” With this law, there’s no one to stop from enforcing it.
S.B. 8 puts ordinary people in charge of law enforcement. Anyone — at all — can sue any individual who “aids or abets,” or even intends to abet, an abortion in Texas after six weeks. Women seeking abortion themselves are exempt, but anyone who advises them (including a spouse), gives them a ride, provides counseling, staffs a clinic, and so on, can be sued by any random stranger. If the plaintiff wins, they pocket $10,000 plus court costs, and the clinic that provided the procedure is closed down. If the defendant doesn’t defend themselves, the court must find them guilty. And if the defendant wins, they get…nothing. Not even attorney’s fees.
So, nuisance lawsuits will ruin abortion providers, along with anyone accused of aiding and abetting — or intending to abet — an abortion. And the enforcers will be ordinary citizens.
Texas also passed House Bill 1927, that allows people to carry handguns without a permit, unless they have been convicted of a felony or domestic violence. The measure was not popular in the state. Fifty-nine percent of Texans — including law enforcement officers — opposed it. But 56% of Republicans supported it.
“I don’t know what it’s a solution to,” James McLaughlin, executive director of the Texas Police Chiefs Association, said to Heidi Pérez-Moreno of the Texas Tribune when Republican governor Greg Abbott signed the bill in mid-August. “I don’t know what the problem was to start with.”
Taken together with the vigilantism running wild in school board meetings and attacks on election officials, the Texas legislation is a top red flag in the red flag factory. The Republican Party is empowering vigilantes to enforce their beliefs against their neighbors.
The law, which should keep us all on a level playing field, has been abandoned by our Supreme Court. It refused to stop the new Texas abortion law from going into effect, and by a 5–4 vote, it issued an opinion refusing to block the law. Justice Sonia Sotomayor’s dissent read: “The court’s order is stunning. Presented with an application to enjoin a flagrantly unconstitutional law engineered to prohibit women from exercising their constitutional rights and evade judicial scrutiny, a majority of Justices have opted to bury their heads in the sand.”
Texas’s law flouts nearly 50 years of federal precedents, she points out, but the Supreme Court has looked the other way. ”The State’s gambit worked,” Sotomayor wrote. She continued: “This is untenable. It cannot be the case that a state can evade federal judicial scrutiny by outsourcing the enforcement of unconstitutional laws to its citizenry.”
The Supreme Court has essentially blessed the efforts of Texas legislators to prevent the enforcement of federal law by using citizen vigilantes to get their way. The court decided the case on its increasingly active “shadow docket,” a series of cases decided without full briefings or oral argument, often in the dead of night, without signed opinions. In the past, such emergency decisions were rare and used to issue uncontroversial decisions or address irreparable immediate harm (like the death penalty). Since the beginning of the Trump administration, they have come to make up the majority of the court’s business.
Since 2017, the court has used the shadow docket to advance right-wing goals. It has handed down brief, unsigned decisions after a party asks for emergency relief from a lower court order, siding first with Trump, and now with state Republicans, at a high rate. As University of Texas law professor Stephen Vladeck noted: “In less than three years, [Trump’s] Solicitor General has filed at least twenty-one applications for stays in the Supreme Court (including ten during the October 2018 Term alone).” In comparison, “during the sixteen years of the George W. Bush and Obama Administrations, the Solicitor General filed a total of eight such applications — averaging one every other Term.”
So, operating without open arguments or opinions, the Supreme Court has shown that it will not enforce federal law, leaving state legislatures to do as they will. This, after all, was the whole point of the “originalism” that Republicans embraced under President Ronald Reagan. Originalists wanted to erase the legal justification of the post–World War II years that used the “due process” and “equal protection” clauses of the Fourteenth Amendment to apply the protections of the Bill of Rights to the states.
It was that concept that protected civil rights for people of color and for women, by using the federal government to prohibit states from enforcing discriminatory laws. Since the 1980s, Republicans have sought to hamstring federal power and return power to the states, which have neither the power nor the inclination to regulate businesses effectively, and which can discriminate against minorities and get away with it, so long as the federal government does not enforce equal protection. That is now a reality.
Worse, though, the mechanisms of the Texas law officially turn a discriminatory law over to state-level vigilantes to enforce. The wedge to establish this mechanism is abortion, but the door is now open for extremist state legislatures to turn to private citizens to enforce any law that takes away an individual’s legal right…like, say, the right to vote. And in Texas, now, a vigilante doesn’t even have to have a permit to carry the gun that will back up his threats.
During Reconstruction, vigilantes also carried guns. They enforced state customs that reestablished white supremacy after the federal government had tried to defend equality before the law. It took only a decade for former Confederates who had tried to destroy the government to strip voting rights, and civil rights, from the southern Black men who had defended the United States government during the Civil War. For the next eighty years, the South was a one-party state where enforcement of the laws depended on your skin color, your gender, and whom you knew.
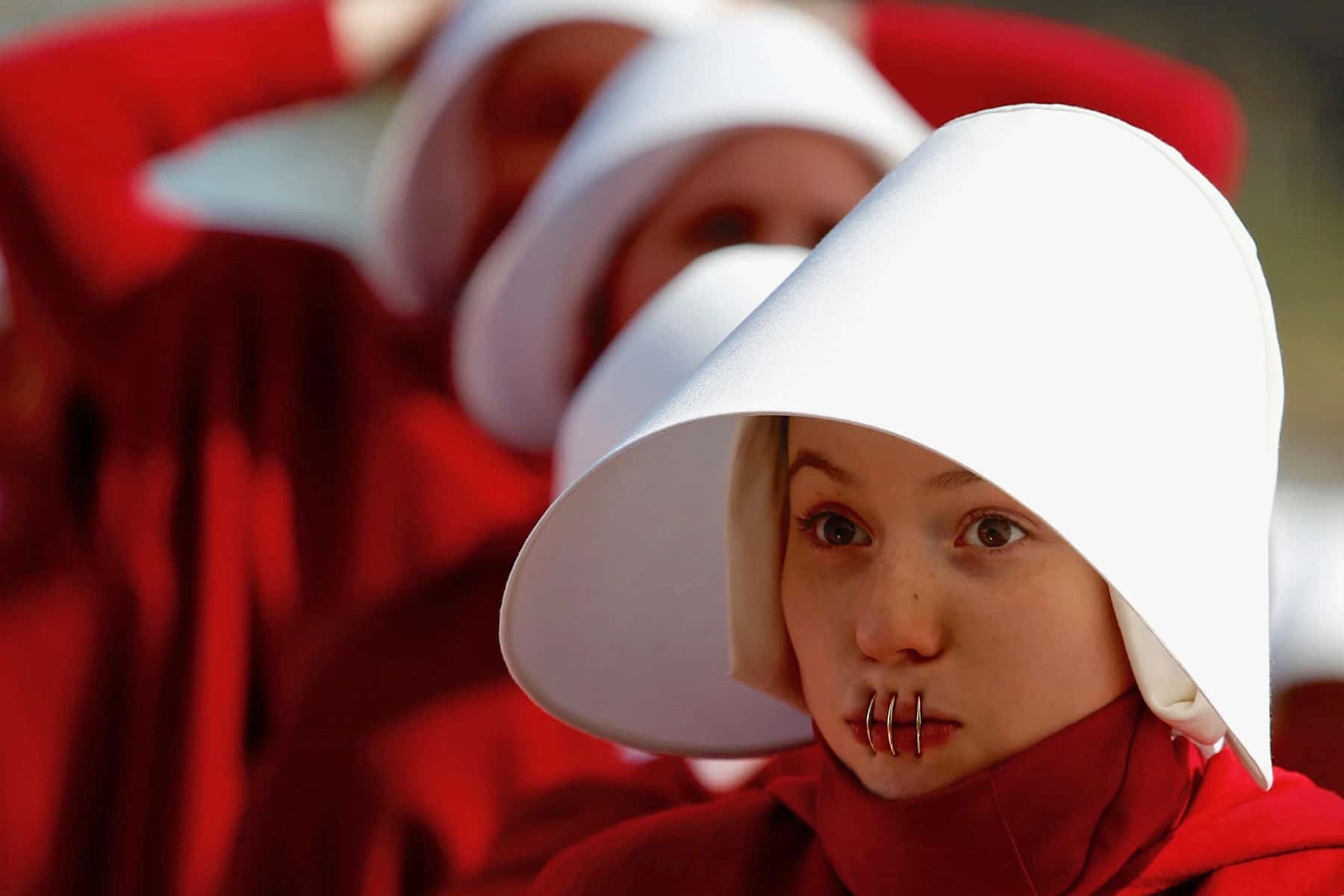
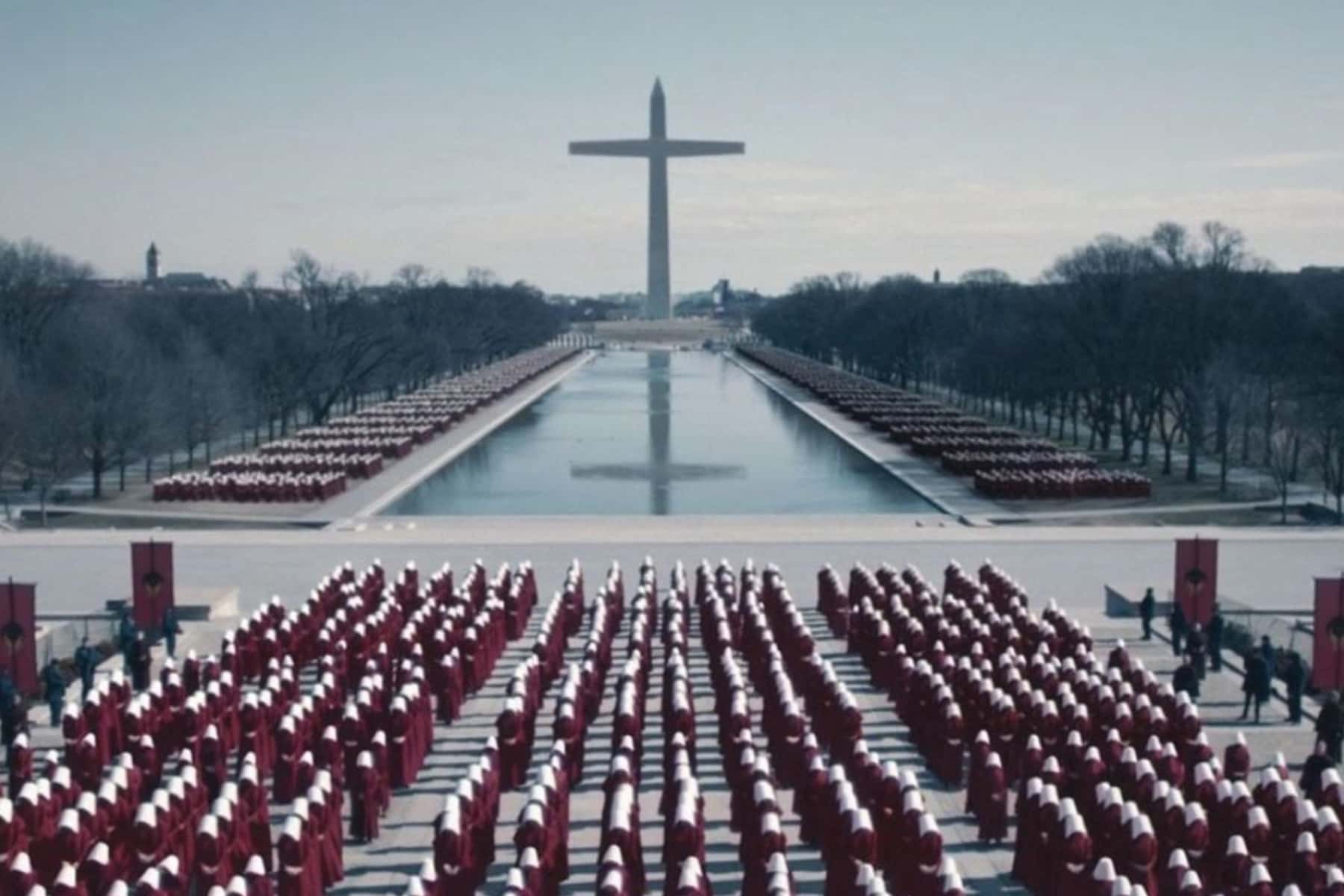
Opponents have compared those who backed the Texas anti-abortion law to the Taliban, the Islamic extremists in Afghanistan whose harsh interpretation of Islamic Sharia law strips women of virtually all rights. But the impulse behind the Texas law, the drive to replace the federal protection of civil rights with state vigilantes enforcing their will, is homegrown.
It is a reflection of the position that Republicans would like women to have in our society, for sure, but it is also written in the laughing faces of Mississippi law enforcement officers Lawrence Rainey and Cecil Ray Price in 1967, certain even as they were arraigned for the 1964 murders of James Earl Chaney, Andrew Goodman, and Michael Henry Schwerner, that the system was so rigged in their favor that they would literally get away with murder. When they were killed, Chaney, Goodman, and Schwerner were trying to register Black people to vote.
As I have said repeatedly, most Americans agree on most issues, even the hot button ones like abortion. A Gallup poll from June examining the issue of abortion concluded that only 32% of Americans wanted the U.S. Supreme Court’s 1973 Roe v. Wade decision overturned, while 58% of Americans opposed overturning it.
“’Overturning Roe v. Wade,’” Lydia Saad of Gallup wrote, “is a shorthand way of saying the Supreme Court could decide abortion is not a constitutional right after all, thus giving control of abortion laws back to the states. This does not sit well with a majority of Americans or even a large subset of Republicans. Not only do Americans oppose overturning Roe in principle, but they oppose laws limiting abortion in early stages of pregnancy that would have the same practical effect.”
While it is hard to remember today, the modern-day opposition to abortion had its roots not in a moral defense of life but rather in the need for President Richard Nixon to win votes before the 1972 election. Pushing the idea that abortion was a central issue of American life was about rejecting the equal protection of the laws embraced by the Democrats far more than it was ever about using the government to protect fetuses.
Abortion had been a part of American life since its inception, but states began to criminalize abortion in the 1870s. By 1960, an observer estimated that there were between 200,000 and 1.2 million illegal U.S. abortions a year, endangering women, primarily poor ones who could not afford a workaround.
To stem this public health crisis, doctors wanted to decriminalize abortion and keep it between a woman and her doctor. In the 1960s, states began to decriminalize abortion on this medical model, and support for abortion rights grew.
The rising women’s movement wanted women to have control over their lives. Its leaders were latecomers to the reproductive rights movement, but they came to see reproductive rights as key to self-determination. In 1969, activist Betty Friedan told a medical abortion meeting: “[M]y only claim to be here, is our belated recognition, if you will, that there is no freedom, no equality, no full human dignity and personhood possible for women until we assert and demand the control over our own bodies, over our own reproductive process….”
In 1971, even the evangelical Southern Baptist Convention agreed that abortion should be legal in some cases, and vowed to work for modernization. Their convention that year reiterated its “belief that society has a responsibility to affirm through the laws of the state a high view of the sanctity of human life, including fetal life, in order to protect those who cannot protect themselves” but also called on “Southern Baptists to work for legislation that will allow the possibility of abortion under such conditions as rape, incest, clear evidence of severe fetal deformity, and carefully ascertained evidence of the likelihood of damage to the emotional, mental, and physical health of the mother.”
By 1972, Gallup pollsters reported that 64% of Americans agreed that abortion was between a woman and her doctor. Sixty-eight percent of Republicans, who had always liked family planning, agreed, as did 59% of Democrats.
In keeping with that sentiment, in 1973, the Supreme Court, under Republican Chief Justice Warren Burger, in a decision written by Republican Harry Blackmun, decided Roe v. Wade, legalizing first-trimester abortion. The common story is that Roe sparked a backlash. But legal scholars Linda Greenhouse and Reva Siegel found something interesting. In a 2011 article in the Yale Law Journal, they showed that opposition to the eventual Roe v. Wade decision began in 1972 — the year before the decision — and that it was a deliberate attempt to polarize American politics.
In 1972, Nixon was up for reelection, and he and his people were paranoid that he would lose. His adviser Pat Buchanan was a Goldwater man who wanted to destroy the popular New Deal state that regulated the economy and protected social welfare and civil rights. To that end, he believed Democrats and traditional Republicans must be kept from power and Nixon must win reelection.
Catholics, who opposed abortion and believed that “the right of innocent human beings to life is sacred,” tended to vote for Democratic candidates. Buchanan, who was a Catholic himself, urged Nixon to woo Catholic Democrats before the 1972 election over the issue of abortion. In 1970, Nixon had directed U.S. military hospitals to perform abortions regardless of state law; in 1971, using Catholic language, he reversed course to split the Democrats, citing his personal belief “in the sanctity of human life — including the life of the yet unborn.”
Although Nixon and Democratic nominee George McGovern had similar stances on abortion, Nixon and Buchanan defined McGovern as the candidate of “Acid, Amnesty, and Abortion,” a radical framing designed to alienate traditionalists.
As Nixon split the U.S. in two to rally voters, his supporters used abortion to stand in for women’s rights in general. Railing against the Equal Rights Amendment, in her first statement on abortion in 1972, activist Phyllis Schlafly did not talk about fetuses; she said: “Women’s lib is a total assault on the role of the American woman as wife and mother and on the family as the basic unit of society. Women’s libbers are trying to make wives and mothers unhappy with their career, make them feel that they are ‘second-class citizens’ and ‘abject slaves.’ Women’s libbers are promoting free sex instead of the ‘slavery’ of marriage. They are promoting Federal ‘day-care centers’ for babies instead of homes. They are promoting abortions instead of families.”
Traditional Republicans supported an activist government that regulated business and promoted social welfare, but radical right Movement Conservatives wanted to kill the active government. They attacked anyone who supported such a government as immoral. Abortion turned women’s rights into murder.
Movement Conservatives preached traditional roles, and in 1974, the TV show Little House on the Prairie started its 9-year run, contributing, as historian Peggy O’Donnell has explored, to the image of white women as wives and mothers in the West protected by their menfolk. So-called prairie dresses became the rage in the 1970s.
This image was the female side of the cowboy individualism personified by Ronald Reagan. A man should control his own destiny and take care of his family unencumbered by government. Women should be wives and mothers in a nuclear family. In 1984, sociologist Kristin Luker discovered that “pro-life” activists believed that selfish “pro-choice” women were denigrating the roles of wife and mother. They wanted an active government to give them rights they didn’t need or deserve.
By 1988, Rush Limbaugh, the voice of Movement Conservatism, who was virulently opposed to taxation and active government, demonized women’s rights advocates as “Femi-nazis” for whom “the most important thing in life is ensuring that as many abortions as possible occur.” The complicated issue of abortion had become a proxy for a way to denigrate the political opponents of the radicalizing Republican Party.
Such threats turned out Republican voters, especially the evangelical base. But support for safe and legal abortion has always been strong, as it remains today. Until yesterday, Republican politicians could pay lip service to opposing the Roe v. Wade decision to get anti-abortion voters to show up at the polls, without facing the political fallout of actually getting rid of the decision. Now, though, Texas has effectively destroyed the right to legal abortion.
The fact that the Fox News Channel was not mentioning what should have been a landmark triumph of its viewers’ ideology suggests Republicans know that ending safe and legal abortion is deeply unpopular. Their base finally, after all these years, got what it wanted. But now the rest of the nation, which had been assured as recently as the confirmation hearings for Supreme Court Justice Brett Kavanaugh that Roe v. Wade was settled law that would not be overturned, gets a chance to weigh in.
Еvy Mаgеs and HυIυ
Letters from an Аmerican is a daily email newsletter written by Heather Cox Richardson, about the history behind today’s politics